Dabcyl acid, SE
CAS No. 146998-31-4
Dabcyl acid, SE( Dabcyl, SE )
Catalog No. M23629 CAS No. 146998-31-4
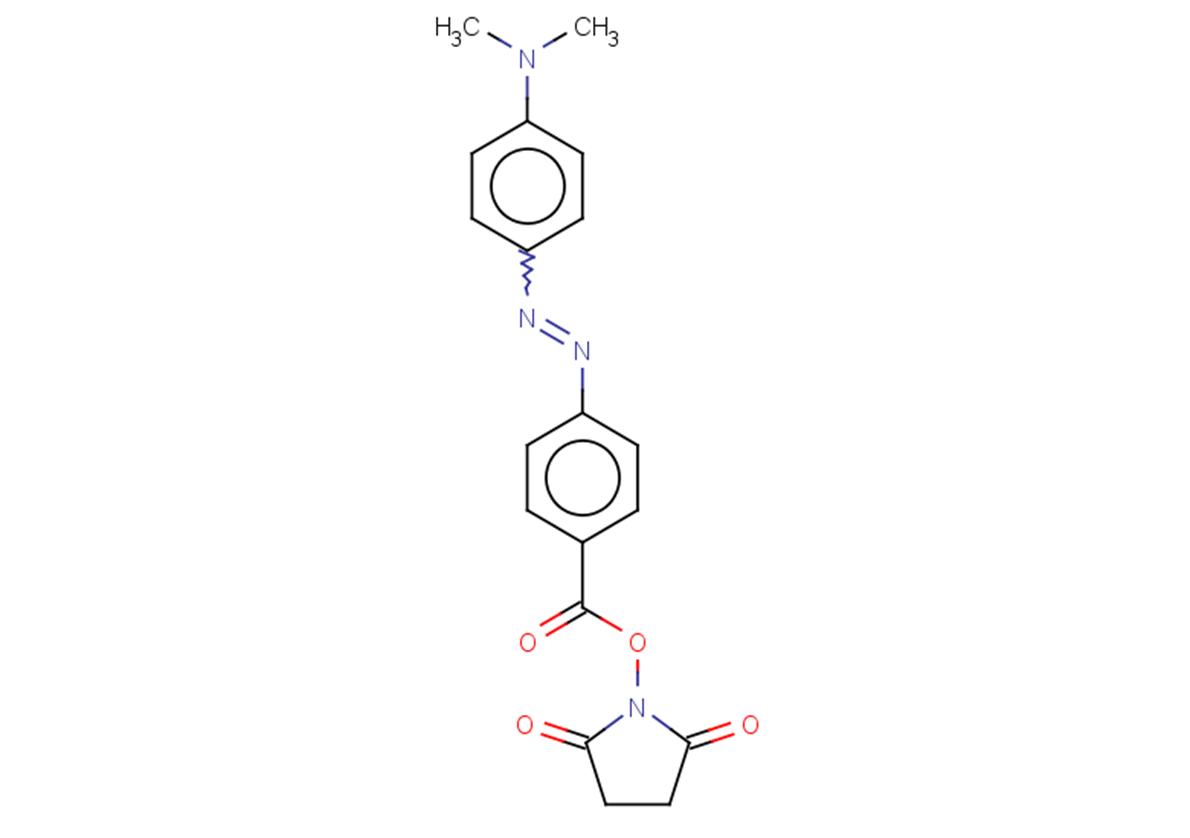
Dabcyl acid, SE is the amino-reactive form of Dabcyl acid and used to prepare a variety of FRET-based probes that contain Dabcyl acid.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDabcyl acid, SE
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDabcyl acid, SE is the amino-reactive form of Dabcyl acid and used to prepare a variety of FRET-based probes that contain Dabcyl acid.
-
DescriptionDabcyl acid, SE is the amino-reactive form of Dabcyl acid and used to prepare a variety of FRET-based probes that contain Dabcyl acid.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsDabcyl, SE
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptorothers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number146998-31-4
-
Formula Weight366.37
-
Molecular FormulaC19H18N4O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:5 mg/mL?(13.64 mM;?Need ultrasonic)
-
SMILESCN(C)c(cc1)ccc1N=Nc(cc1)ccc1C(ON(C(CC1)=O)C1=O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Saikosaponin B1
Saponin activator. Activates release of Prostaglandin E2 in vitro. Anti-inflammatory agent. Orally active. Active in vivo and in vitro.
-
Pancreatic Polypepti...
Pancreatic Polypeptide, avian
-
2,4,6-trichlorol-3-m...
2,4,6-Trichlorol-3-methyl-5-methoxy-phenol 1-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 6)-β-d-glucopyranoside is a chlorophenyl glycoside that is commonly found in the bulbs of Lilium brownie var. viridulum.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


